Final Blog
Final Blog
- Final Score
- Question I missed
- Blog about the quiz
- Night of the Museum Blog
Final Score
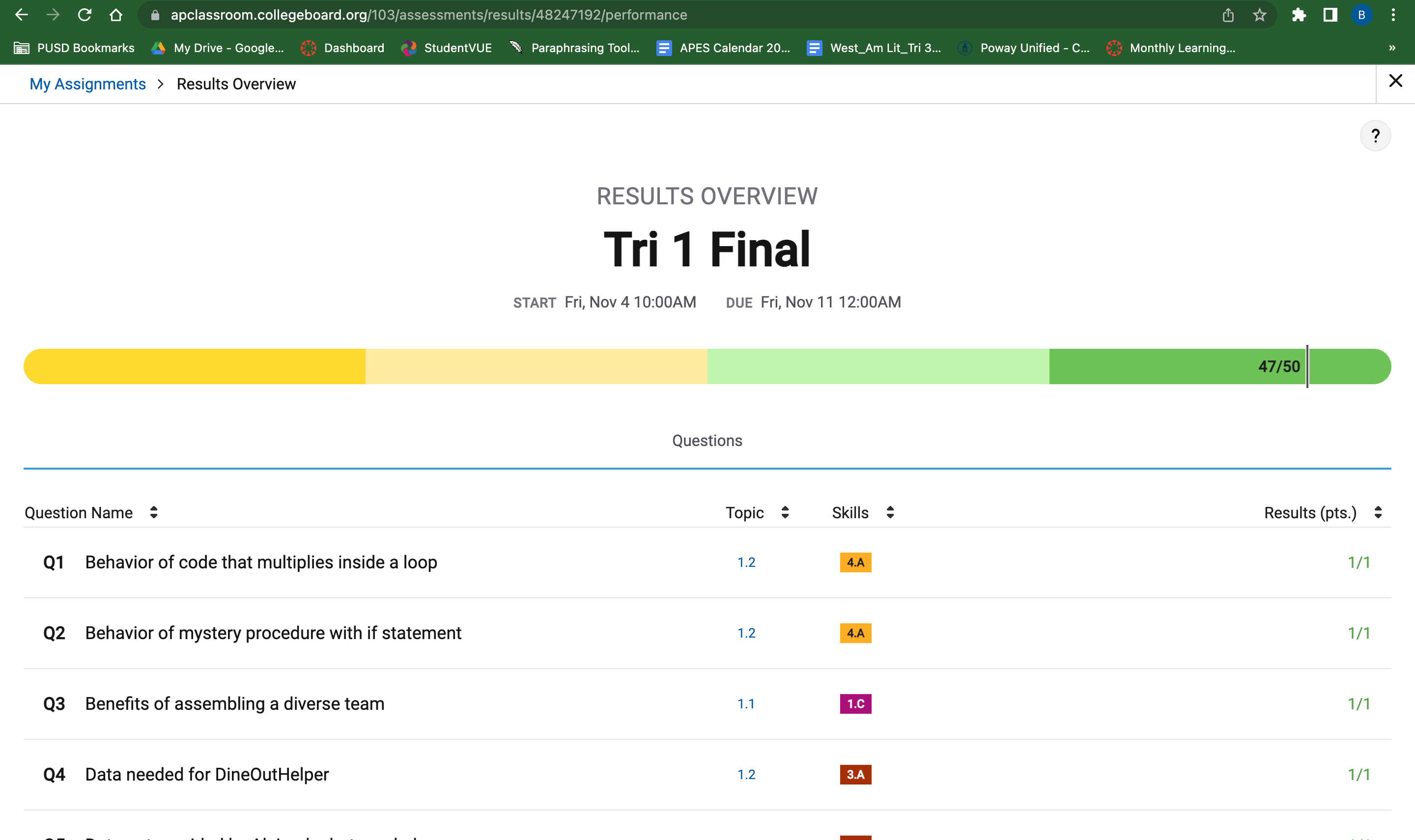
Question I missed
Question 35
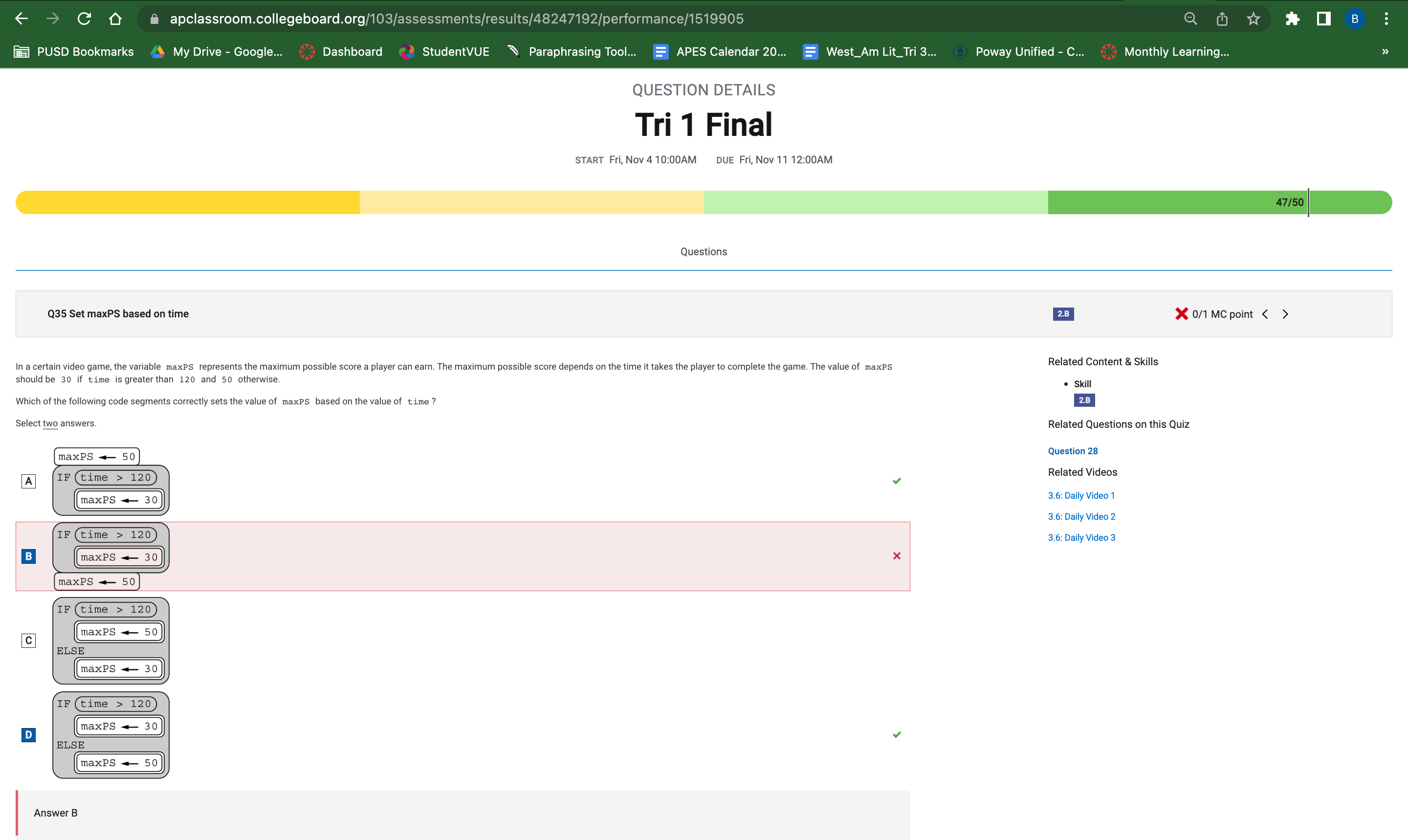
This question asked me to select two answers that correctly set the value of maxPS based on the value of time. The answer was A and D but I answered with B and D. I knew that answer D was correct because it used the IF statement to set maxPS to 30 when time was less than 120 and uses the ELSE statement to set maxPS to 50 otherwise. I though B was correct by having the maxPS to 50 at the end but I didn’t know that having it at the end automatically sets it to 50 regardless of the value. This would mean A is correct because it sets the value to 50 at the start and if it meets the requirements for the IF statement, it runs through it.
Question 48
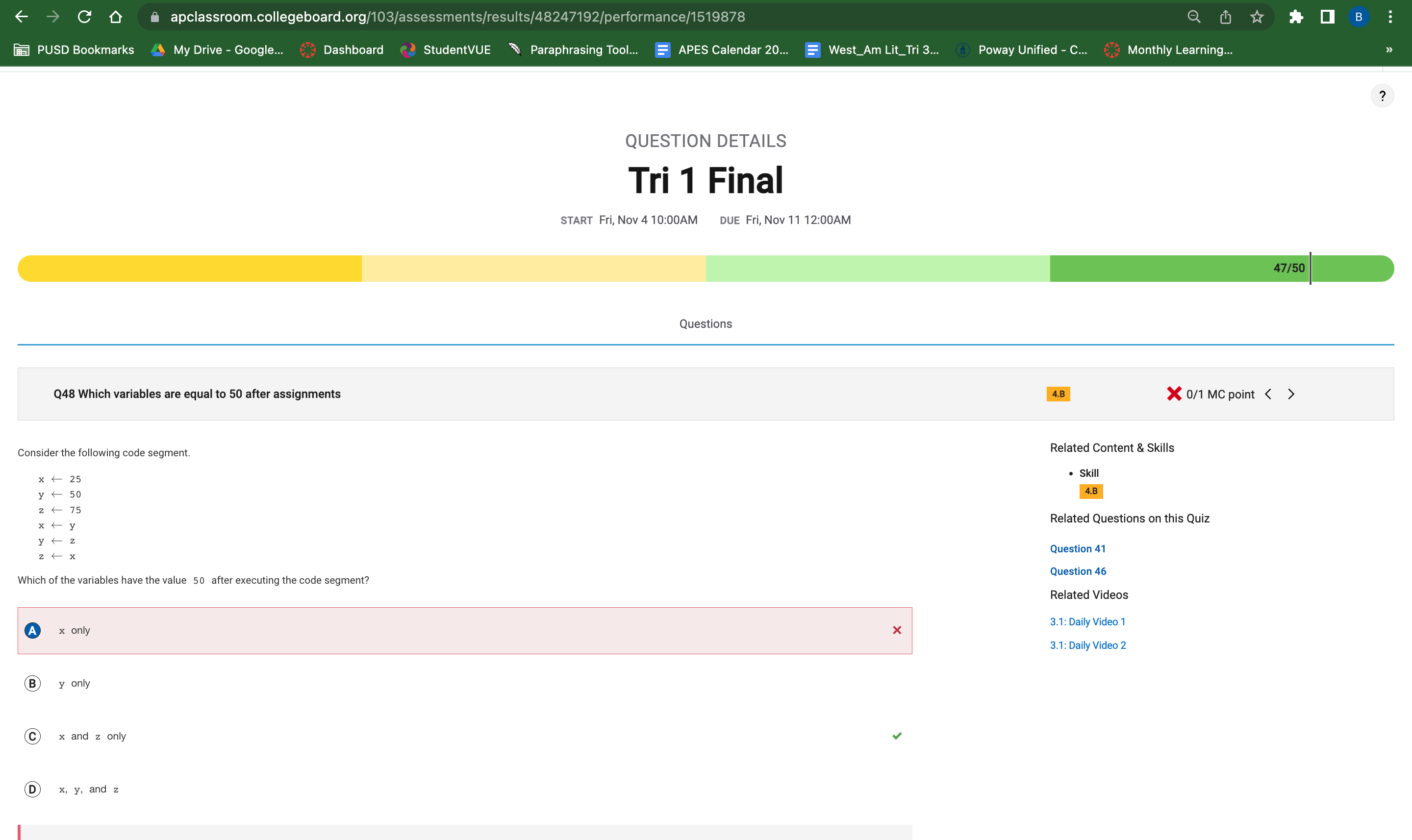
This question asked me to identify which variable had a value of 50 after doing the code segment. The answer was C but I answered with A. I kew that the variable x had a value of 50 because in the fourth line of the code it said that x <- y and y was equal to 50 so that meant x would be 50. However, I forgot the when running the code, the variables change as it goes through the code segments. This led me to think that variable z was only 25 because I forgot that the variable x was changed in the fourth line to 50.
Question 49
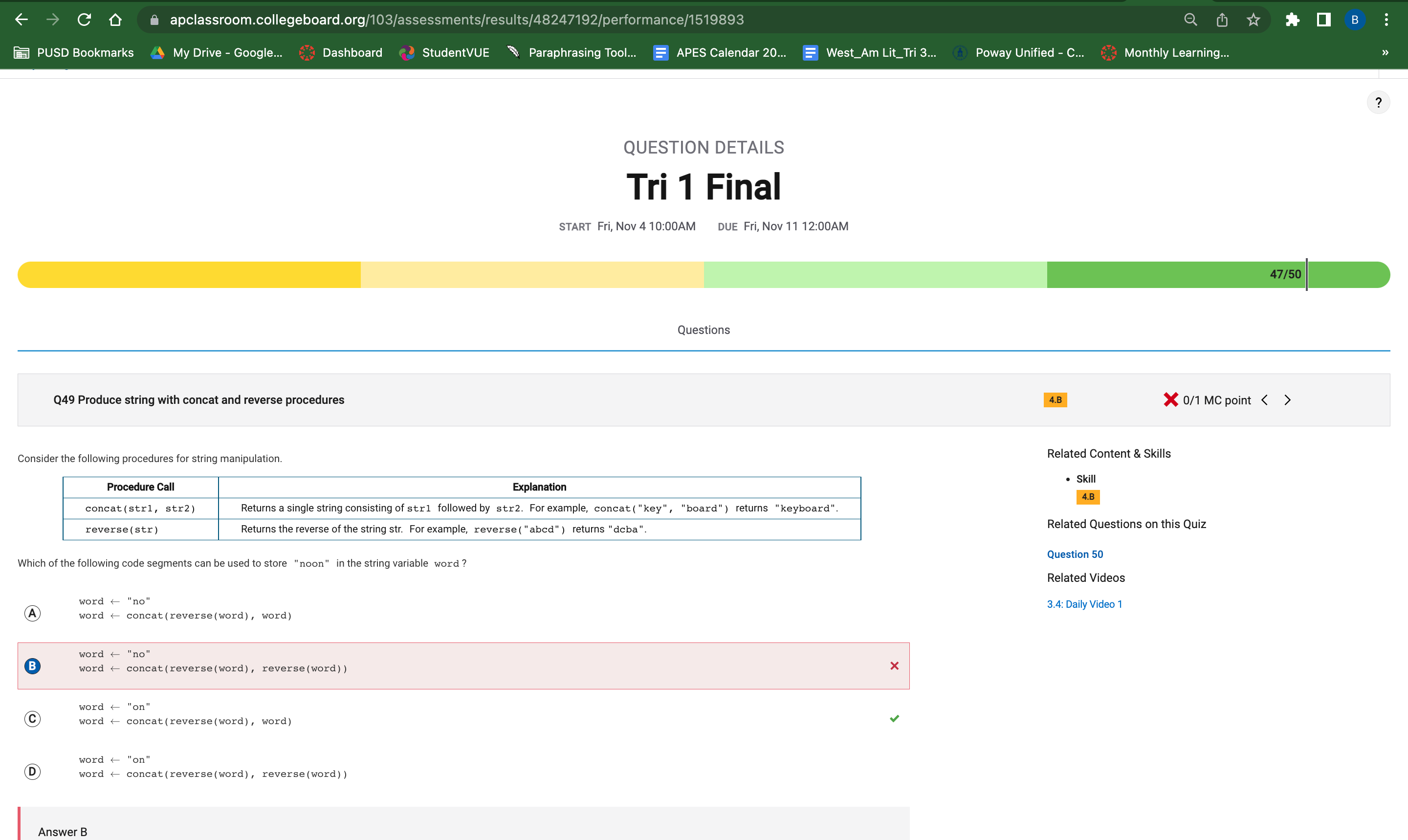
This question asked me to identify which code segment could be used to store “noon” in the string variable word. THe answer was C but I answered with B. I honestly just misread the answer and thought it said word and not reverse word. This meant that the output would be onon instead of noon. Answer C is correct because it starts with the word on, then it reverses the word to no and then it prints the starting word on to combine to make noon.
Blog about the quiz
Overall, I thought this test was pretty straight forward because I took my time with every question and understood what it was asking me. I also had some knowledge from watching most of the college board videos while taking notes of them.
Here are some of the notes:
1.1 Collaboration Notes
Daily Video 1
- Innovations are improved through collaboration in CSP
- A computing innovation includes a program as an integral part of its function
- Effective collaboration skills: Communication, consensus building, conflict resolution, negotiation
- Computing innovation: reflects the diversity of talents and unique perspectives of all the programers who worked to create it
- Collaboration on projects can reduce bias since there are various perspectives Video Quiz:
Daily Video 2
- How computing innovations are developed by groups of people
- Consultation and communication between peers is important
- Information contributed from all the group members can help understand the purpose of the program and create one that incorporates all the perspectives
- Online tools can help collaboration such as pair programming
- Pair programming: work together in pairs- the driver writes the code, the navigator reviews it
- Think pair share: students work through a problem alone then pair with a partner then share with class
- It is important to give credit
1.2 Program Function and Purpose Notes
Daily Video 1
- It is important to know and be able to describe the purpose of a computing innovation
- The purpose could be to solve problems, pursue interests through creative expression, etc.
- Truly understanding the purpose of a program helps the developer(s) develop the program better
Daily Video 2
- Identify inputs/outputs to a program
- Program inputs are data sent to a computer for processing by a program. Some forms can be: tactile, audio, visual, text
- An event is associated with an action and supplies input data to a program
- Events can be generated when a key is pressed, a mouse clicked, etc. Can be any defined action that affects the flow of execution
- Inputs generally affect the output of a program
- In a program, the code is made in a way that after an action, the code “jumps” to the code segment according to the event
- Program’s output is based off input or prior state
Daily Video 3
- A program (software) is a collection of program statements the performs a specific task when run by a computer.
- A code segment is a collection of program statements that is a part of a program
- Software needs to work for a variety of inputs
- The behavior is how the program functions during execution and if often described by how a user can interact with it.
- Can be described broadly by what it does or in detail on how the program accomplishes its function
- A program is a collection of statements: A statement is a single command, a group of statements is a code segment, code segments are executed -> a program/software
1.3 Program Design and Development Notes
Daily Video 1
- Use a development process to develop a program
- Design a program and its user interface
- A development process can be ordered and intentional or exploratory in nature
- Common phases when developing a program: investigating and reflecting, designing, prototyping, testing
- Requires refinement and revision based on feedback, testing, and reflection: may require revisiting phases
- Break the project into smaller pieces and make sure each piece works before adding it to the whole
- Investigate to determine requirements, constraints, concerns and interests of customer
- Investigate by: collecting data through surveys, user testing, interviews, direct observations
- Requirements describe how a program functions and may include a description of user interactions that a program should provide
- Design phase that outlines how to accomplish a program’s goal may include: brainstorming, planning/story boarding, organizing the program into modules and functional components, creation of diagrams, develop testing strategy
- Constantly test your program
Daily Video 2
- When developing a program, it is important to cite and acknowledge code segments used from either another source or developed collaboratively
- When acknowledging someone else, include the origin of code or authors name in the program documentation
- Team of people usually work on a program by each focusing on different functional components
- Each member’s work should be credited in program documentation Sometimes credit is given with comments in the code
- Many developers use code segments, procedures, algorithms made by others who aren’t part of the project so it is important to credit them
Daily Video 3
- Describe the purpose of a code segment or program by writing documentation
- Program documentation: a written description of the function of a code segment, event, procedure, or program and how it was developed EX: comments (don’t effect how the program runs)
- Should actively document throughout development to help development as well as maintaining correct programs
- Program documentation created to: describe the program, list specifications, describe different parts of the program, list of contributors
- Document process: beginning: list specifications, during: keep track of progress, after: explain overall process
- Documentation improves: programming process efficiency, ability to test and refine program, responding to bugs
1.4 Copy of Identifying and Correcting Errors Notes
Daily Video 1
- identify an error
- a logic error is a mistake in the algorithm or program that causes it to behave incorrectly or unexpectedly
- a syntax error is a mistake in the program where the rules of the programming language are not followed
- a run time error is a mistake in the program that occurs during the execution of the program. Programming language define their own runtime errors
- A overflow error is an error that occurs when a computer attempts to handle a number that is outside of the defined range of values
Daily Video 2
- correct the error
- The following are effective ways to find and correct errors
- tests cases
- hand tracing
- visualizations
- debuggers
- adding extra output statements
Daily Video 3
- Identify inputs and corresponding expected outputs or behaviors that can be used to check the correctness of an algorithm or program
- In the development process, testing uses defined inputs to ensure that an algorithm or program is producing the expected outcomes
- Programmers use the results from testing to revise their algorithms or programs
- Defined inputs used to test a program should demonstrate the different expected outcomes that are at or just beyond the extremes of input data
- Program requirements are needed to identify appropriate defined inputs for testing
4.1 The Internet
Daily Video 1
- We have created smaller computers
- Even though it is easier to do now, it is still hard to do it alone
- Computers can receive and send data
- Packet: Small amount of data sent over a network
- Every packet has a source and destination for the information
- Computer system: A group of computing devices and programs working together for a joint purpose
- Computer network: A group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending or receiving data (type of computing system)
- Packet switching: A file that is broke up into packets, sent in any order, and reassembled by the recipient’s device
- Path: Sequence of directly connected computing devices from the sender to the receiver
- Routing: Finding a path
- Bandwidth: Max amount of data sent into a fixed amount of time on a computer network
Daily Video 2
- Internet is a computing network that has interconnected networks the use standardized, open communication protocols
- To access the internet, you need to connect to a computing device to an Internet connected device
- Protocol: Set of rules that were agreed on about the behavior of a system (they are open)
- Internet was designed to be scalable
- Information is passed through data streams
- Data streams have data that is in packets
- Packets can be received in order, out of order, or not at all
- IP, UDP, and TCP are all common protocols
- World Wide Web is a system of links, programs, and files
- HTTP is used by the world wide web and is a protocol
- World wide web uses the internet
Night of the Museum Blog
As I was walking around, I went to another Computer Science group and the AP photography class. Something cool that I saw for the computer science class was that their website was very interactive and I could make comments, like the comments, and generate new quotes. This was very cool to see because I am pretty new to computer science, so being able to see things that I could potentially make in the future is very exciting. For the AP photography class I saw many detailed pictures, but the one that stood out to me the most was a black and white picture of a horse in a field with a mountain in the background. It stood out to me because the horse was perfectly centered in the middle of the photo with a beautiful mountain in the back. The black and white also made the picture stand out because it was the only photo that wasn’t color.